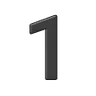Chiffre Un 1
Signification du symbole
The Arabic digit one belongs to the numerals which are widely spread around the planet. This positional counting system appeared in India in the 5th century or even earlier. The Arabs borrowed it from the Indians. Al-Khwarizmi wrote a book called «On the Indian Calculation,» which helped to spread the Arabic digits. Later this counting system came to Europe through Spain. Pope Sylvester II advocated for the replacement of Roman numerals with Arabic ones in the 10th century. In the 12th century, Al-Khwarizmi's book «On the Indian Calculation» was translated into Latin, which played an important role in the adoption of Arabic numerals.
Le symbole «Chiffre Un» est inclus dans le sous-bloc «Chiffres ASCII» du bloc «Latin de base» et a été approuvé dans le cadre de la version Unicode 1.1 en 1993.
Choisissez un style d’image pour l’emoji et affichez-le en grande taille. Toutes les images peuvent être téléchargées et utilisées dans vos créations et présentations.
🛈 Les images d’emoji sont la propriété de leurs détenteurs de droits respectifs. Uniquement pour l’aperçu. Veuillez toujours respecter les conditions de licence de chaque fournisseur.
🛈 Images sous licence ouverte. Téléchargement et utilisation gratuits conformément aux conditions de {{licence}}. Une attribution peut être requise.
| Nom Unicode | Digit One |
| Numéro Unicode | |
| Plan | 0: Plan multilingue de base |
| Bloc Unicode | Latin de base |
| Sous-bloc Unicode | Chiffres ASCII |
| Version Unicode | 1.1 (1993) |
| Code Alt |
| Type de support de miroir jumelé (bidi) | None |
| Exclusion de composition | No |
| Changement de cas | 0031 |
| Changement de boîtier simple | 0031 |
| ID_Continue | + |
| XID_Continue | + |
| Grapheme_Base | + |
| scripts | Common |
| Hex_Digit | + |
| ASCII_Hex_Digit | + |
| Encodage | hex | dec (bytes) | dec | binary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTF-8 | 31 | 49 | 49 | 00110001 |
| UTF-16BE | 00 31 | 0 49 | 49 | 00000000 00110001 |
| UTF-16LE | 31 00 | 49 0 | 12544 | 00110001 00000000 |
| UTF-32BE | 00 00 00 31 | 0 0 0 49 | 49 | 00000000 00000000 00000000 00110001 |
| UTF-32LE | 31 00 00 00 | 49 0 0 0 | 822083584 | 00110001 00000000 00000000 00000000 |
Copiez et collez ces codes pour utiliser le personnage Chiffre Un dans du texte sur des sites web, des réseaux sociaux, des messageries ou des articles de blog.
| HTML | |
| CSS | |
| JavaScript, JSON | |
| Unix, C, PHP, JAVA | |
| Ruby, PHP | |
| Perl | |
| URL-encode |
-
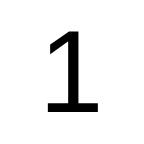 Arimo
Arimo -
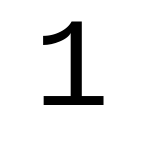 Cousine
Cousine -
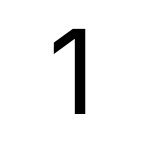 Inter
Inter -
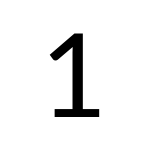 Lato
Lato -
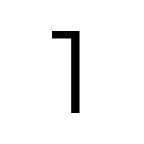 Montserrat
Montserrat -
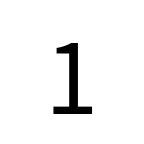 Noto Sans Jp
Noto Sans Jp -
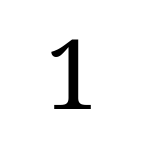 Noto Serif
Noto Serif -
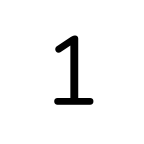 Nunito
Nunito -
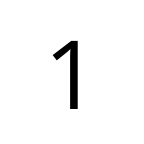 Open Sans
Open Sans -
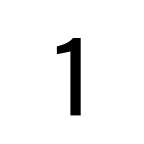 Oswald
Oswald -
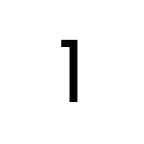 Poppins
Poppins -
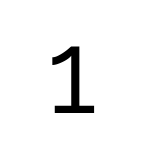 Raleway
Raleway -
 Roboto
Roboto -
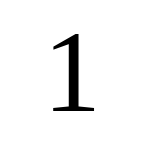 Tinos
Tinos