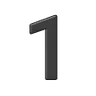Digit One 1
Significato del simbolo
The Arabic digit one belongs to the numerals which are widely spread around the planet. This positional counting system appeared in India in the 5th century or even earlier. The Arabs borrowed it from the Indians. Al-Khwarizmi wrote a book called «On the Indian Calculation,» which helped to spread the Arabic digits. Later this counting system came to Europe through Spain. Pope Sylvester II advocated for the replacement of Roman numerals with Arabic ones in the 10th century. In the 12th century, Al-Khwarizmi's book «On the Indian Calculation» was translated into Latin, which played an important role in the adoption of Arabic numerals.
Il simbolo «Digit One» è incluso nel sotto-blocco «Cifre ASCII» del blocco «Latino di base» ed è stato approvato come parte della versione Unicode 1.1 nel 1993.
Scegli uno stile di immagine per l’emoji e aprilo a grandezza intera. Tutte le immagini possono essere scaricate e utilizzate nei tuoi progetti e presentazioni.
🛈 Le immagini emoji sono di proprietà dei rispettivi titolari dei diritti. Solo per anteprima. Rispetta sempre i termini di licenza di ciascun fornitore.
🛈 Immagini con licenza aperta. Download e utilizzo gratuiti secondo i termini di {{licence}}. Potrebbe essere richiesta l’attribuzione.
| Nome Unicode | Digit One |
| Numero Unicode | |
| Piano | 0: Piano multilingua principale |
| Blocco Unicode | Latino di base |
| Sottoblocco Unicode | Cifre ASCII |
| Versione Unicode | 1.1 (1993) |
| Codice Alt |
| Tipo di supporto specchio accoppiato (bidi) | None |
| Esclusione della composizione | No |
| Cambio di caso | 0031 |
| Semplice cambio di caso | 0031 |
| ID_Continue | + |
| XID_Continue | + |
| Grapheme_Base | + |
| scripts | Common |
| Hex_Digit | + |
| ASCII_Hex_Digit | + |
| Codifica | hex | dec (bytes) | dec | binary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTF-8 | 31 | 49 | 49 | 00110001 |
| UTF-16BE | 00 31 | 0 49 | 49 | 00000000 00110001 |
| UTF-16LE | 31 00 | 49 0 | 12544 | 00110001 00000000 |
| UTF-32BE | 00 00 00 31 | 0 0 0 49 | 49 | 00000000 00000000 00000000 00110001 |
| UTF-32LE | 31 00 00 00 | 49 0 0 0 | 822083584 | 00110001 00000000 00000000 00000000 |
Copia e incolla questi codici per usare il personaggio Digit One nei testi di siti web, social media, messaggistica o post di blog.
| HTML | |
| CSS | |
| JavaScript, JSON | |
| Unix, C, PHP, JAVA | |
| Ruby, PHP | |
| Perl | |
| URL-encode |
-
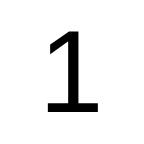 Arimo
Arimo -
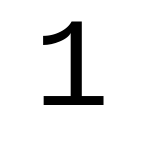 Cousine
Cousine -
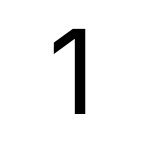 Inter
Inter -
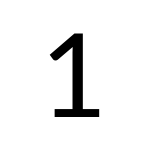 Lato
Lato -
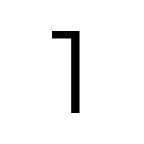 Montserrat
Montserrat -
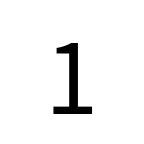 Noto Sans Jp
Noto Sans Jp -
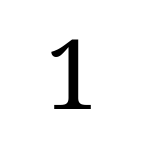 Noto Serif
Noto Serif -
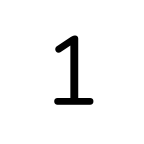 Nunito
Nunito -
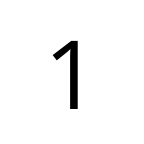 Open Sans
Open Sans -
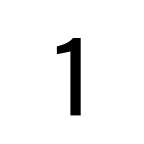 Oswald
Oswald -
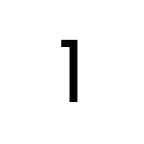 Poppins
Poppins -
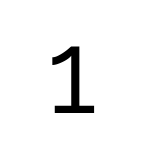 Raleway
Raleway -
 Roboto
Roboto -
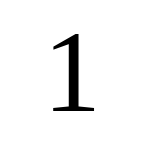 Tinos
Tinos