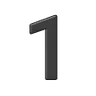Digit One 1
Symbol Meaning
The Arabic digit one belongs to the numerals which are widely spread around the planet. This positional counting system appeared in India in the 5th century or even earlier. The Arabs borrowed it from the Indians. Al-Khwarizmi wrote a book called “On the Indian Calculation,” which helped to spread the Arabic digits. Later this counting system came to Europe through Spain. Pope Sylvester II advocated for the replacement of Roman numerals with Arabic ones in the 10th century. In the 12th century, Al-Khwarizmi's book “On the Indian Calculation” was translated into Latin, which played an important role in the adoption of Arabic numerals.
The symbol “Digit One” is included in the “ASCII digits” subblock of the “Basic Latin” block and was approved as part of Unicode version 1.1 in 1993.
Pick an emoji image style and open it for a high resolution preview. Open licensed emoji images can be downloaded and used in your designs and presentations.
🛈 Emoji artwork is the property of its respective owners. Preview only. Please follow each vendor’s license.
🛈 Open-licensed artwork. Free to download and use under the terms of {{licence}}. Attribution may be required.
| Unicode Name | Digit One |
| Unicode Number | |
| Plane | 0: Basic Multilingual Plane |
| Unicode Block | Basic Latin |
| Unicode Subblock | ASCII digits |
| Unicode Version | 1.1 (1993) |
| Alt Code |
| Type of paired mirror bracket (bidi) | None |
| Composition Exclusion | No |
| Case change | 0031 |
| Simple case change | 0031 |
| ID_Continue | + |
| XID_Continue | + |
| Grapheme_Base | + |
| scripts | Common |
| Hex_Digit | + |
| ASCII_Hex_Digit | + |
| Encoding | hex | dec (bytes) | dec | binary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UTF-8 | 31 | 49 | 49 | 00110001 |
| UTF-16BE | 00 31 | 0 49 | 49 | 00000000 00110001 |
| UTF-16LE | 31 00 | 49 0 | 12544 | 00110001 00000000 |
| UTF-32BE | 00 00 00 31 | 0 0 0 49 | 49 | 00000000 00000000 00000000 00110001 |
| UTF-32LE | 31 00 00 00 | 49 0 0 0 | 822083584 | 00110001 00000000 00000000 00000000 |
Copy and paste these codes to use the Digit One character in text for websites, social media, messengers, or blog posts.
| HTML | |
| CSS | |
| JavaScript, JSON | |
| Unix, C, PHP, JAVA | |
| Ruby, PHP | |
| Perl | |
| URL-encode |
-
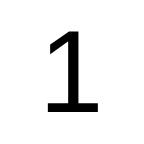 Arimo
Arimo -
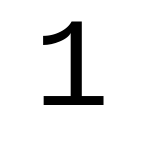 Cousine
Cousine -
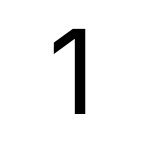 Inter
Inter -
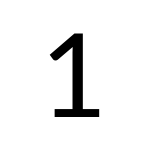 Lato
Lato -
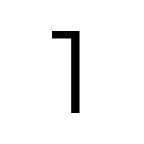 Montserrat
Montserrat -
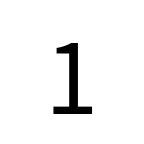 Noto Sans Jp
Noto Sans Jp -
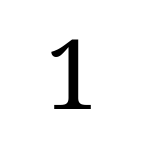 Noto Serif
Noto Serif -
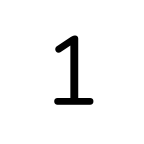 Nunito
Nunito -
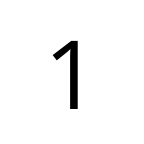 Open Sans
Open Sans -
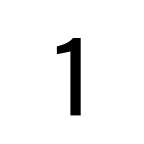 Oswald
Oswald -
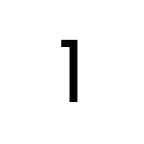 Poppins
Poppins -
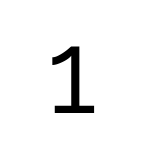 Raleway
Raleway -
 Roboto
Roboto -
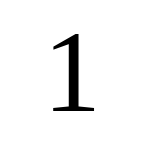 Tinos
Tinos